Description
Polyethylene glycol
General Information
The medical, chemical, and industrial fields benefit the most from Polyethylene glycol‘s (PEG) multiple uses. PEG is a biocompatible, synthetic, hydrophilic polyether molecule. The wide variety of molecular weights and weight distributions found in PEGs result from their synthesis via ring-opening polymerization of ethylene oxide. Linear, branching, Y-shaped, and multi-arm PEGs are all possible during PEG synthesis. To make PEGs usable for crosslinking and conjugation chemistry, the terminal hydroxyl end group can be modified to several reactive functional end groups. PEG is a biocompatible synthetic substance that is water-soluble and easy to work with. PEG is a non-volatile, non-toxic, inert, colorless, odorless chemical that doesn’t evaporate. It dissolves easily in water and a wide variety of organic solvents, including benzene, carbon tetrachloride, and chloroform. Diethyl ether and hexane, however, are insoluble in PEG.
Usage of Polyethylene glycol
Polyethylene glycol PEG has shown benefits in medicine both on its own and as a means of altering the properties of biomolecules, nanocarriers, surfaces, and drugs. PEG is often used as a laxative and sold under the brand name Macrogol. Because of its osmotic pressure, ingested PEG can have a laxative effect by attracting water into the waste material. PEG is also used in blood banks to concentrate antibodies by removing water from the system in a low ionic strength saline solution. The low protein affinity of PEGylated materials makes them suitable for extended periods of circulation within the body without provoking an immune response. Some studies involving the selective capture of proteins may also benefit from these characteristics. To fight hemophilia, researchers have found that they may drastically shorten bleeding durations in animal studies by selectively binding coagulation factor VIII.
Hydrophilic characteristics such as those possessed by Polyethylene glycol have proven effective in avoiding non-specific protein adhesion in single-molecule fluorescence investigations. Finally, numerous uses employ PEG as a filler in paints and lubricants due to PEG compounds’ inert and non-toxic character. PEG’s ability to inhibit clumping and enhance particle separation makes it a useful binding and dispersing agent.
| Applications |
| Medicine (biomolecules, nanocarriers, surfaces, and drugs)
Blood Banks (concentrate antibodies) To fight hemophilia As a filler in paints and lubricants |
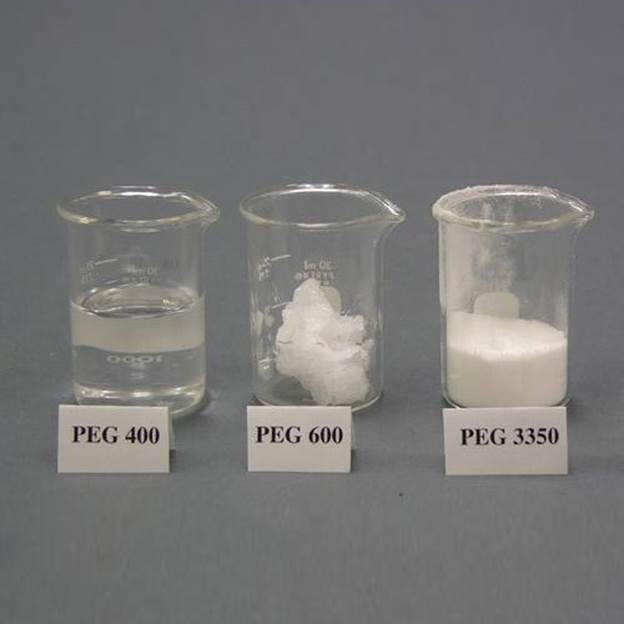
Three forms of PEG
Technical data sheet & Chemical Formula
The medical, chemical, and industrial fields benefit the most from polyethylene glycol‘s (PEG) multiple uses. PEG is a biocompatible, synthetic, hydrophilic polyether molecule. Molecularly, it can be written as H(O)(CH2)n(OH). Let’s look at the specifications.
| Physical State | Solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Odor Threshold | No information available |
| pH | 5.0-7.0 |
| Melting Point/Range | 55 – 60 °C / 131 – 140 °F |
| Boiling Point/Range | No information available |
| Flash Point | 270 °C / 518 °F |
| Evaporation Rate | Not applicable |
| Flammability (solid,gas) | Flammability (solid,gas) No information available |
| Flammability or explosive limits | |
| Upper | No data available |
| Lower | No data available |
| Vapor Pressure | No information available |
| Vapor Density | Not applicable |
| Specific Gravity | No information available |
| Solubility | No information available |
| Partition coefficient; n-octanol/water | No data available |
| Autoignition Temperature | 305 °C / 581 °F |
| Decomposition Temperature | No information available |
| Viscosity | Not applicable |
Packing of Polyethylene glycol
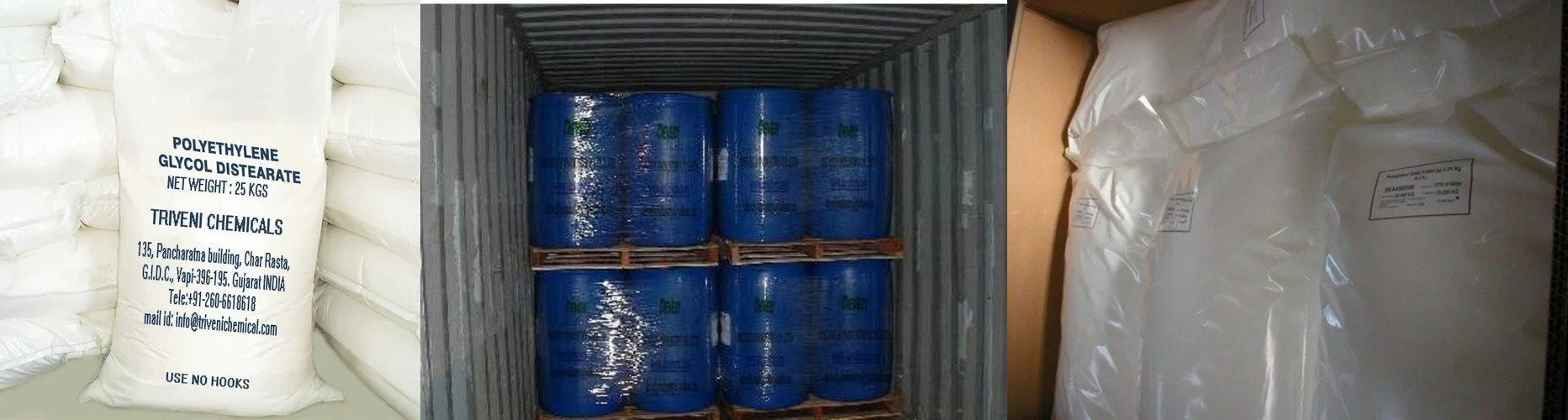

Packing
Polyethylene glycol is available in three main forms: powder, liquid, and solid flakes. The powder form is usually packed in 25 to 1000 kg bags (PP bags, for example). The liquid form is generally packed in 230 to 1000 kg and even more DRUMs (barrels). The solid flakes are usually packed in 10 to 1000 kg bags.
Safety & warning & transportation of Polyethylene glycol
This product contains no substances that could be dangerous. If you get any in your eyes, wash them well for at least 15 minutes, making sure to get beneath your eyelids. Find a doctor immediately. If you get skin contamination, wash off with lots of water for at least 15 minutes. If you have any of these stated symptoms, seek medical assistance immediately. To get some air, go outside. If symptoms appear, get medical assistance right once. After ingestion, rinse your mouth thoroughly with water and consume lots of fluids. If signs like these develop, you should see a doctor immediately. When dealing with this, ensure you have safety gear, including a mask. Maintain a healthy airflow. Wear protective gloves if you have to handle them, and keep them away from your skin, eyes, and clothing. Store in a dry, cool, ventilated area with tightly closed containers. Transporting it doesn’t call for any unique preparations.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.